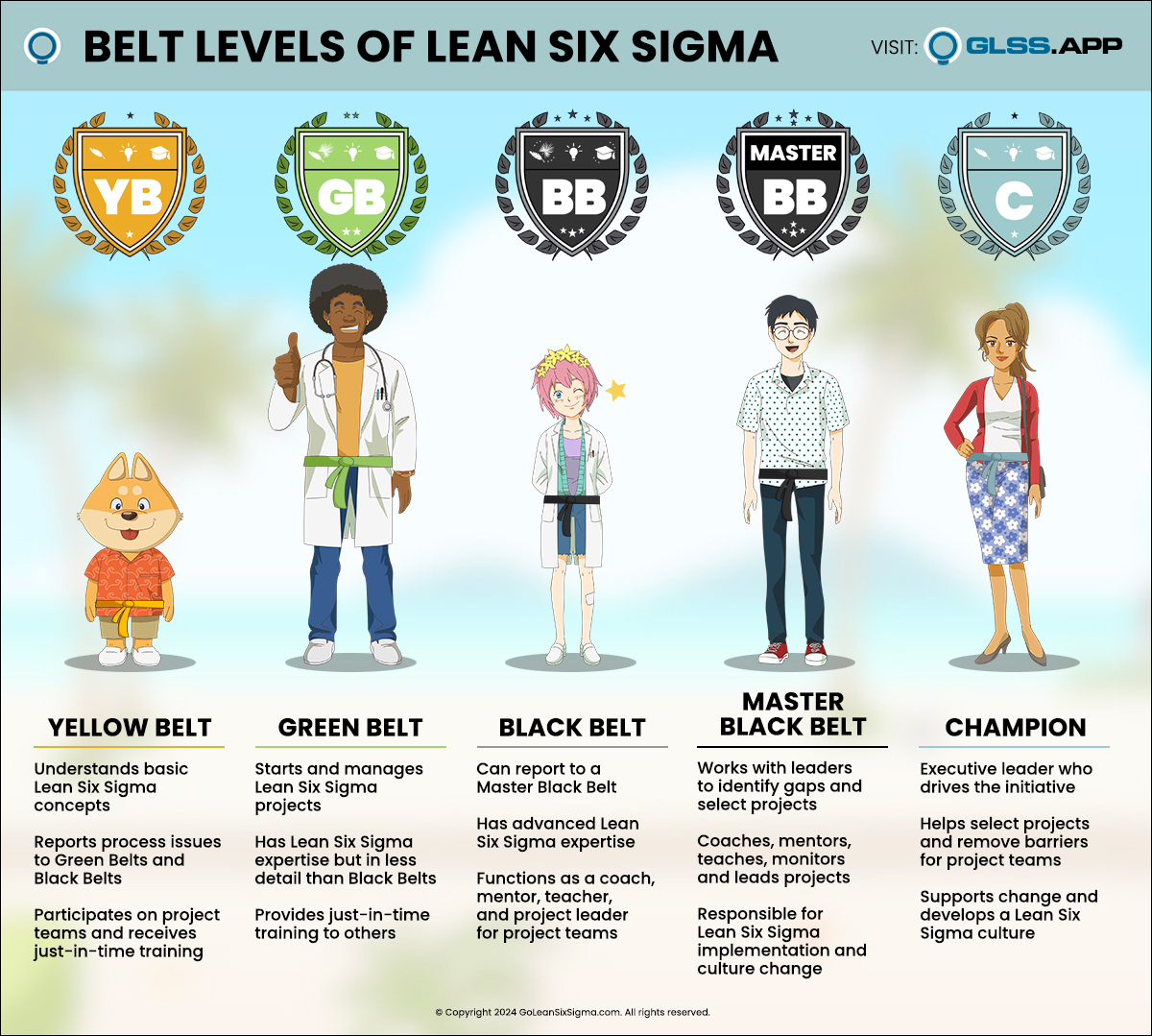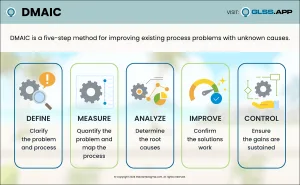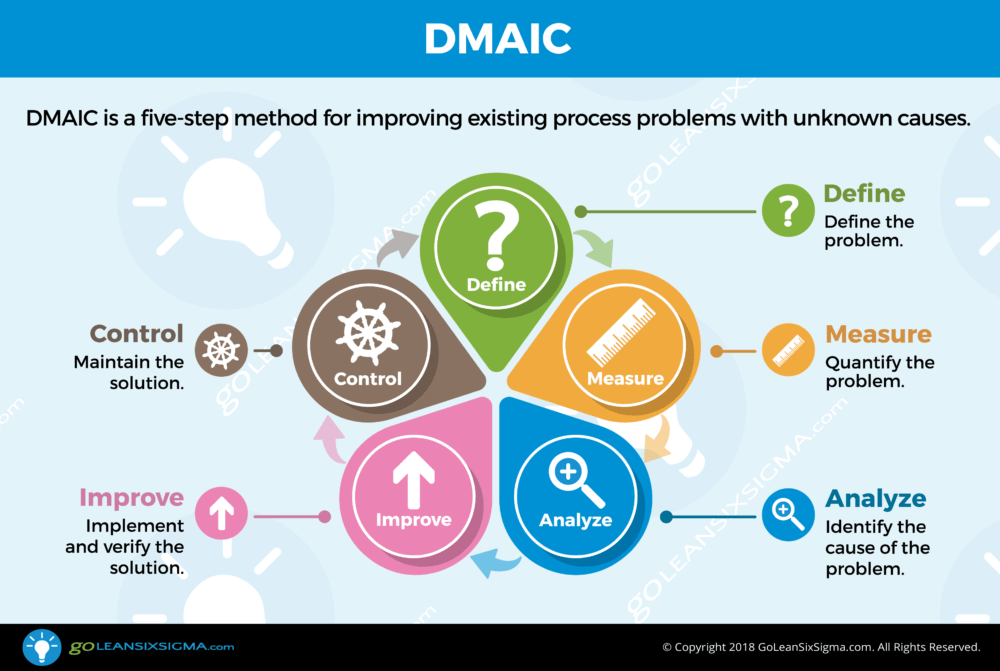

Lean Six Sigma is simply a process for solving a problem. It consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, & Control. This process is also known as DMAIC (“duh-may-ik”), its acronym. DMAIC is a five-step method for improving existing process problems with unknown causes.
Phase 1: Define
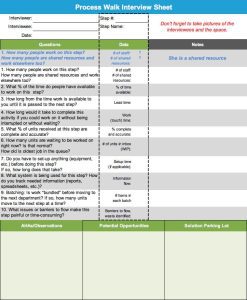
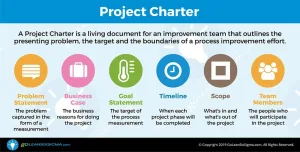
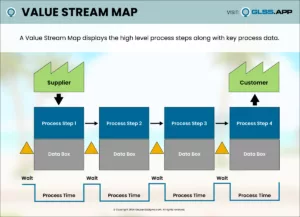
Define the problem. What problem would you like to fix? The Define Phase is the first phase of the Lean Six Sigma improvement process. In this phase the project team creates a Project Charter, a high-level map of the process and begins to understand the needs of the customers of the process. This is a critical phase in which the team outlines the project focus for themselves and the leadership of the organization.
- Define the Problem by Developing a “Problem Statement”
- Define the Goal by Developing a “Goal Statement”
- Define the Process by Developing Process Maps
- Define the Customer and Their Requirements
- Inform Others of Project Progress
Phase 2: Measure
Quantify the problem. How does the process currently perform? Or in other words, what is the magnitude of the problem? Measurement is critical throughout the life of the project. As the team starts collecting data they focus on both the process as well as measuring what customers care about. That means initially there are two focuses: reducing lead time or improving quality. In the Measure Phase, the team refines the measurement definitions and determines the current performance or the baseline of the process.
- Determine How the Process Currently Performs
- Create a Plan to Collect the Data
- Ensure the Data is Reliable
- Gather the Baseline Data
- Update Your Project Charter
Phase 3: Analyze
Identify the cause of the problem. What is causing the problem? The Analyze Phase is often not given enough attention and, without analysis, teams jump to solutions before knowing the true root causes of the issues. The result is teams who implement solutions but don’t resolve the problem! These efforts waste time, consume resources, create more variation and, often cause new problems. The ideal is for teams to brainstorm potential root causes (not solutions), develop hypotheses as to why problems exist and then work to prove or disprove their hypotheses. Verification includes both process analysis and data analysis and has to be completed before implementing solutions. This is the crux of the Analyze Phase!
- Closely Examine the Process
- Graphically Display the Data
- Look for What Might be Causing the Problem
- Verify the Cause(s) of the Problem
- Update Your Project Charter
Phase 4: Improve
Implement and verify the solution. How will the team mitigate the root causes of the problem? Once the project teams have determined the root causes it’s time to develop solutions. The Improve Phase is where the team brainstorms solutions, pilots process changes, implements solutions and lastly, collects data to confirm there is measurable improvement. A structured improvement effort can lead to innovative and elegant solutions that improve the baseline measure and, ultimately, the customer experience.
- Brainstorm Solutions That Might Fix the Problem
- Select the Practical Solutions
- Develop Maps of Processes Based on Different Solutions
- Select the Best Solution(s)
- Implement the Solution(s)
- Measure to Ensure Improvement
Phase 5: Control
Maintain the solution. How do you sustain the improvement? Now that the process problem is fixed and improvements are in place, the team must ensure that the process maintains the gains. In the Control Phase the team is focused on creating a Monitoring Plan to continue measuring the success of the updated process and developing a Response Plan in case there is a dip in performance. Once in place, the team hands these plans off to the Process Owner for ongoing maintenance.
- Ensure the Process Is Properly Managed and Monitored
- Document the Improved Process
- Apply Improvements to Other Areas
- Share and Celebrate Your Success
- Continuously Improve the Process Using Lean Principles

Start Your Free Training
Check out our free Yellow Belt Training to start your improvement journey today!
What’s next?
- Lean Six Sigma Training & Certification
- What Is Lean Six Sigma?