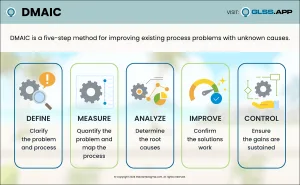
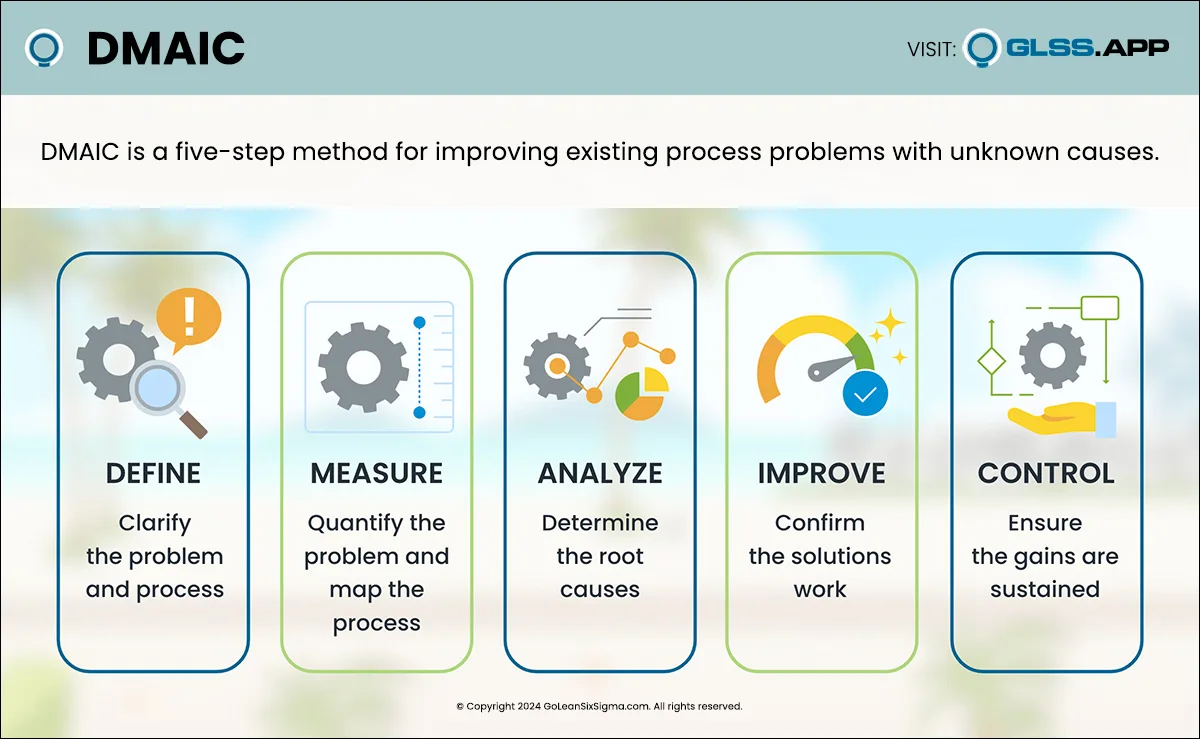
DMAIC is the problem-solving approach that drives Lean Six Sigma. It’s a five-phase method—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control—for improving existing process problems with unknown causes. DMAIC is based on the Scientific Method and it’s pronounced “duh-may-ik.”
Originally published on August 24th, 2017, this article was updated and republished on January 11th, 2024.

To build your understanding of the method, and help you apply it to solve process problems, we’ve broken down the DMAIC Phases for you.
Before Starting DMAIC: Select a Good Project
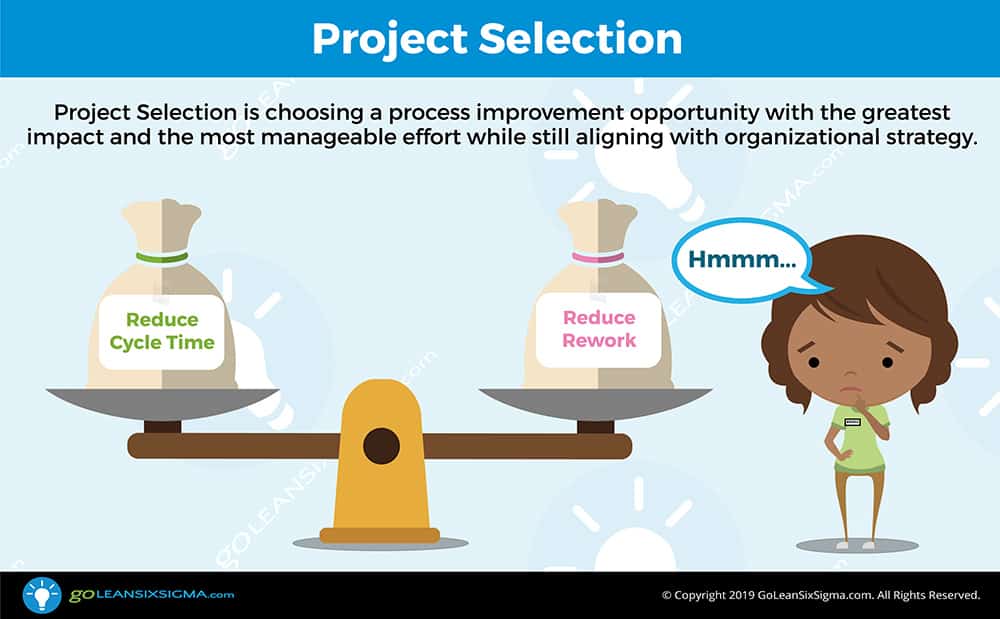
The focus of any process improvement effort is selecting the right project. Good candidates for improvement will set you up for success with DMAIC. Here are 4 key guidelines:
- Choose an obvious problem within an existing process
- Choose something that would make a difference but would not be overly complex to address—Meaningful but Manageable
- Make sure there is potential to reduce lead time or defects while resulting in cost savings or improved productivity
- Check if you can collect data about the selected process—you want to achieve Measurable improvement
Once you’ve selected a good project, you and your improvement team can apply DMAIC to dig into process issues and deliver quantifiable, sustainable results.
Now, on to the DMAIC process!
Define
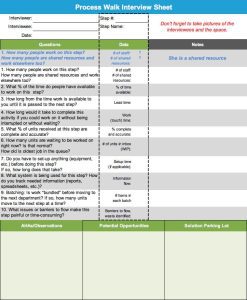
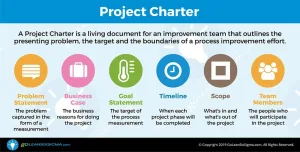
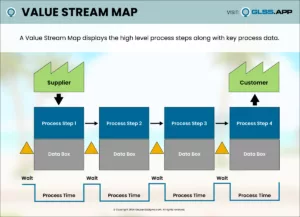
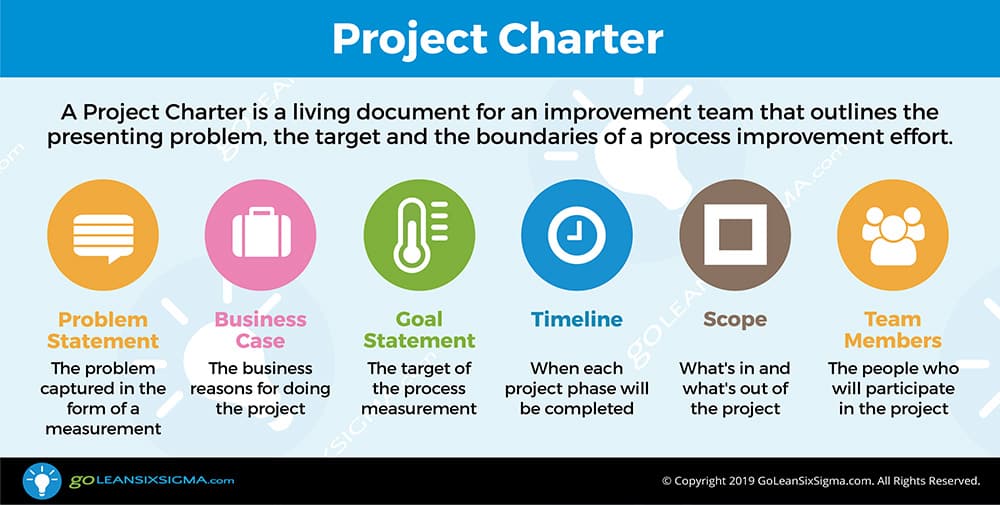
What problem would you like to fix? Define is the first phase of the Lean Six Sigma improvement process. During this phase the project team drafts a Project Charter, plots a high-level map of the process and clarifies the needs of the process customers. By conducting Process Walks and talking to process participants they begin their journey of building their process knowledge. Before moving on to the Measure Phase, the team refines their project focus and ensures they’re aligned with the goals of organizational leadership.
[Learn More: Define Phase]Measure
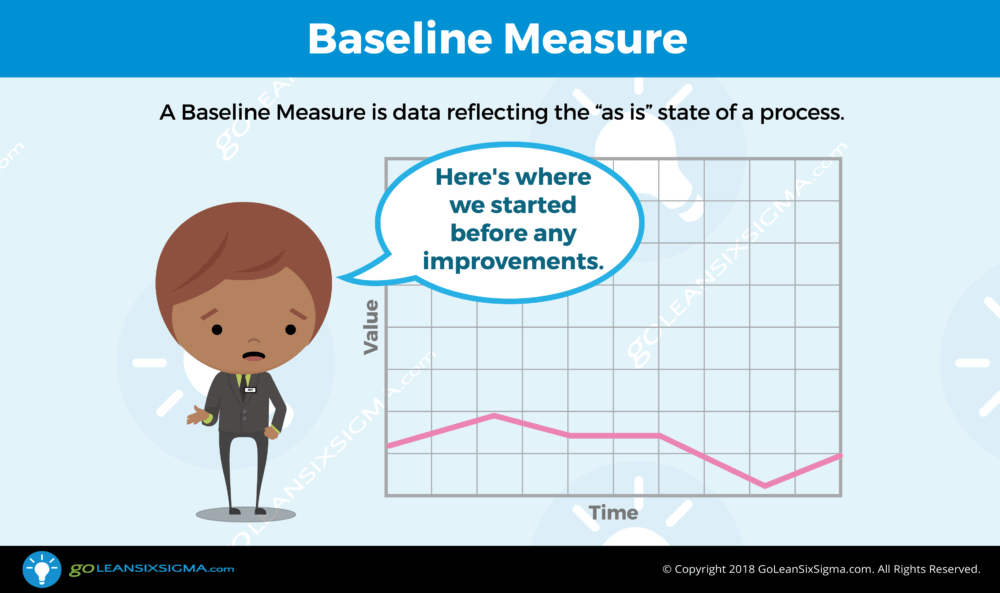
How does this process currently perform? What is the magnitude of the problem? Measurement is critical throughout the life of the project since it provides key indicators of process health and clues to where process issues are happening. As the team collects data they focus on the lead time of the process or the quality of what customers are receiving from the process. Before moving on to the Analyze Phase, the team defines their measures and determines the current performance or the baseline of the process.
[Learn More: Measure Phase]Analyze
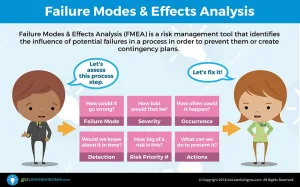
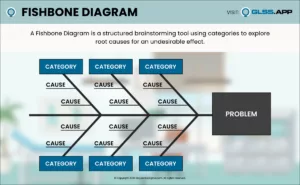
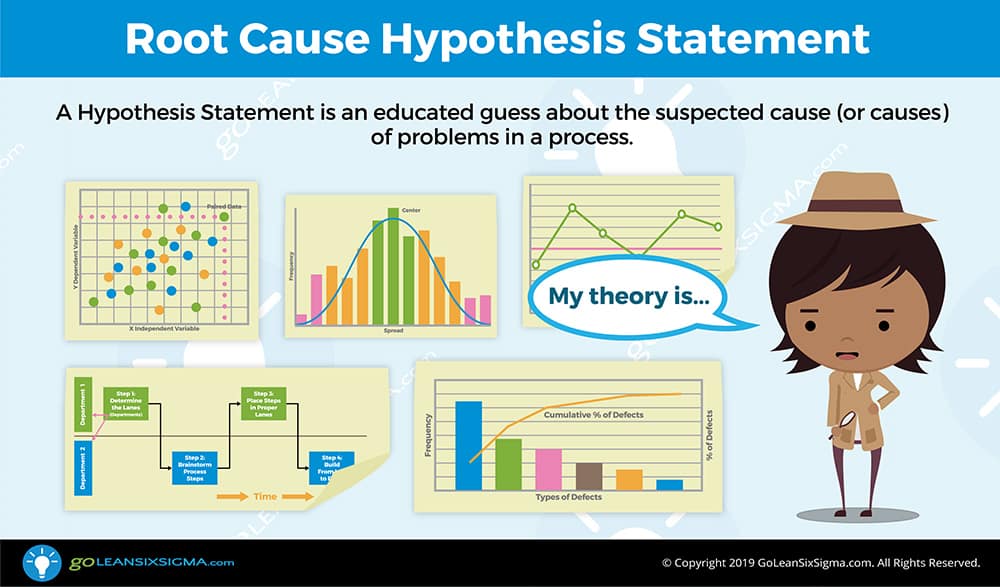
What is causing the problem? One of the biggest challenges for teams is resisting the urge to jump to solution before understanding the true root causes of process issues. Without proper analysis, teams can implement solutions that don’t resolve the issue—this wastes time, consumes resources, increases variation and risks causing new problems. Have you seen teams do this? Yes, it happens all the time! Instead of implementing solutions that don’t solve the problem, the ideal is for teams to learn from their Process Walks, study their charts and graphs and use their observations to develop and confirm theories about what’s causing the issue they’re trying to fix. The crux of this phase is to verify hypotheses before implementing solutions. Only then should the team move to the Improve Phase!
[Learn More: Analyze Phase]Improve
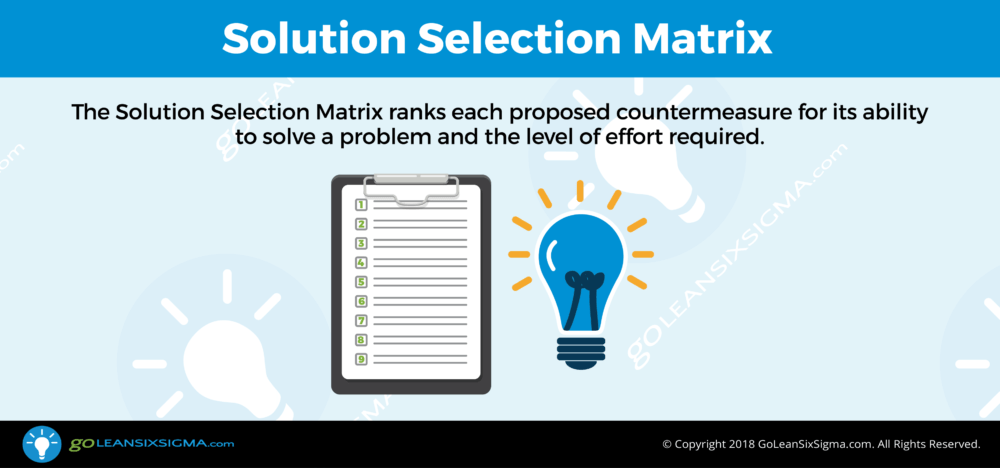
How will the team fix the root causes of the problem? Once they have determined what’s causing the problem, it’s time for the team to implement plans to resolve the root cause(s). The Improve Phase is where the team refines their countermeasure ideas, pilots process changes, implements solutions and lastly, collects data to confirm there is measurable improvement. A structured improvement effort can lead to innovative and elegant changes that improve the baseline measure and, ultimately, the customer experience.
[Learn More: Improve Phase]Control
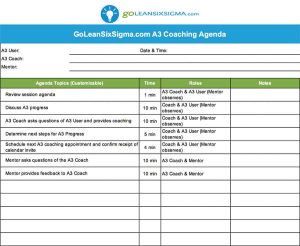
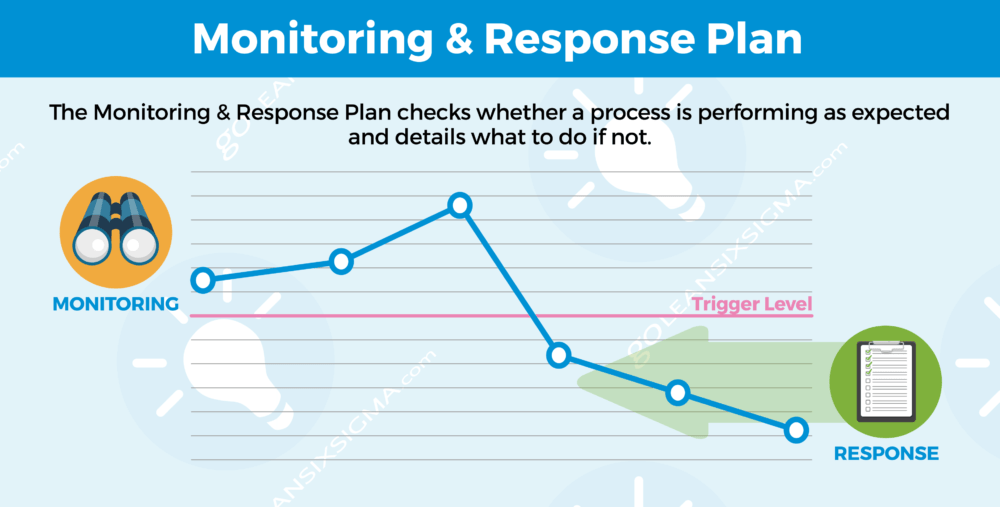
How do you sustain the improvement? With improvements in place and the process problem fixed, the team must work to maintain the gains and make it easy to update best practices. In the Control Phase, the team develops a Monitoring Plan to track the success of the updated process and crafts a Response Plan in case there is a dip in performance. Once in place, the Process Owner monitors and continually updates the current best method.
[Learn More: Control Phase]Lean Six Sigma: DMAIC In-Depth

Get Green Belt Training & Certification to learn how to begin applying Lean Six Sigma and start improving processes immediately!