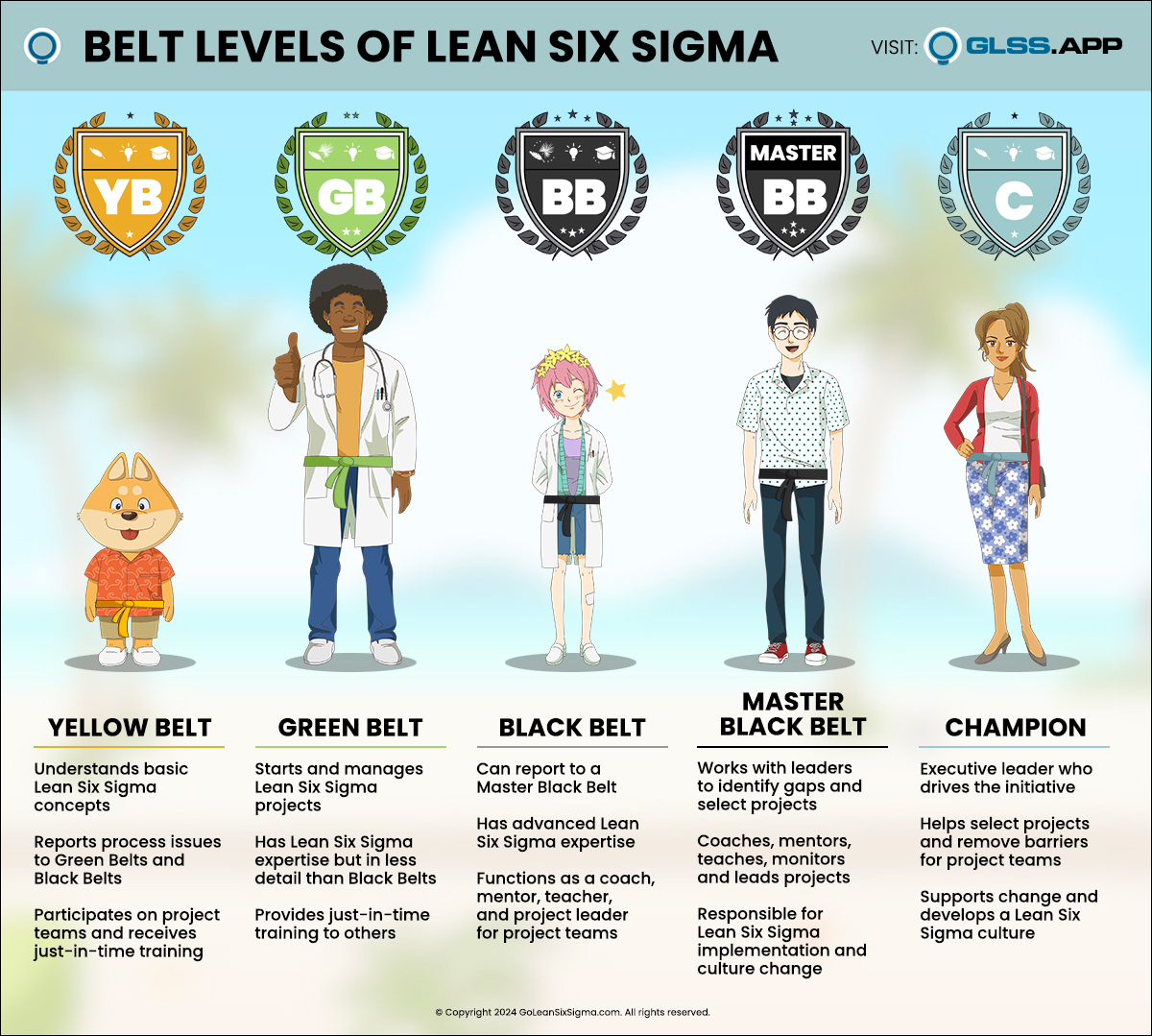
What Is the Black Belt Exam?
The Black Belt Exam is a key step towards Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification. Having passed the GoLeanSixSigma.com Green Belt Exam, this will serve as a test of your understanding of the more advanced concepts and tools of DMAIC. You will be expected to demonstrate your mastery of the terminology along with when, how and where to use the complete set of Black Belt concepts and tools.
Online Exam Format
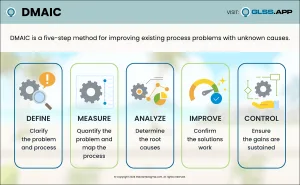
The exam consists of 5 sections with 185 multiple-choice questions total. The sections included are:
- Introduction & Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
Exam Setup
The exam is an online, open-book test but designed to be taken individually. Please do not work with others in order to complete the exam.
The exam is divided into the 5 sections listed previously and each section has a time limit based on the number and complexity of questions in the section. You will complete each section one at a time. You will have 5 hours total to complete the exam.
Method of Scoring
All questions are weighted equally. You must achieve at least 80% in each of the 5 sections in order to pass the exam as a whole. You will be notified of your grade at the end of each section and.
If you do not pass one or more sections, you may retake only those sections that scored under 80%. You are allowed unlimited retakes.
Types of Questions
Questions can be posed in different ways:
- What: This requires that you demonstrate that you can recall the definition of the concept or tool in question and are able to show general knowledge of the concept.
- When or Why: This requires that you are able to identify when during a project to use the concept or tool in question and what presenting scenarios would call for them. This will involve assessing sample case studies and determining next steps.
- How: This requires that you demonstrate your understanding of the series of steps and components involved in using a particular concept or tool. Examples would include setting up a test, calculating a formula, running an experiment or constructing a chart. This will also involve sample case studies with questions designed to evaluate this skill.
- Application: This requires that you demonstrate your ability to interpret the results of a given case study.
Sample Questions
Below are samples of the types of questions you will see on the test.
- Which of the following would be included as good criteria for project selection?
- Alignment with organizational mission
- Potential for positive customer impact
- Level of support from leadership
- All of the above
- Which of the following is true regarding continuous data?
- It can represent categories
- It always has a normal distribution
- It often requires some kind of gage in order to be measured
- It generally requires larger sample sizes than discrete data
- A One-Sample T-Test is a hypothesis that is designed to compare the difference between:
- The defect rates of two different data sets
- The average of a normal continuous data set and a standard
- The variation of two or more data sets
- The median of a continuous data set and a standard
- An improvement team was interested in experimenting to see which application form results in the fewest errors. Which of the following would best describe the method the team would use?
- One Factor at a Time
- Full Factorial
- Fractional Factorial
- None of the above
- An improvement team is interested in tracking the customer hang-ups per day as a percent of the total calls received by the call center per day. Given their monitoring needs, the best chart for their Control Plan would be the:
- U Chart
- P Chart
- nP Chart
- C chart
Areas of Expertise
Questions in the Black Belt Exam are based on the broadly accepted criteria for the skills and knowledge of a Black Belt. These are the specific, advanced skills that have been added to basic Green Belt skills. This exam covers only these advanced Black Belt skills. The criteria have been created to ensure a balance of Lean and Six Sigma capabilities that are essential in order to improve the internal efficiency, the client experience while leading others in the organization to achieve its mission.
The key concepts and tools you are expected to know are listed below. The goal is to score at least 80% on each section of the exam. You are not expected to know everything, but you should demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the tools and concepts associated with a Black Belt level of expertise. If you are confident in your knowledge of the material listed then you are ready to take the exam!
Introduction Section
This section tests for understanding and comprehension of how to select projects, a advanced problem-solving model and the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in becoming a Black Belt.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Project Selection
- List the criteria necessary for effective project selection
- Distinguish between well-selected projects and those that are not
- Explain how to align projects with organizational objectives and purpose
- Describe Dashboards and Scorecards and the kinds of measures they contain
- List the different types of projects and when to apply them (DMAIC, DMADV, DFSS and Quick Wins)
- Process Improvement Model
- Explain why and when to use the PDCA Model
- Distinguish between the DMAIC method and PDCA
- List the steps involved in PDCA
- Leadership Skills
- Describe the different levels of coaching required of Black Belts and what makes a good coach
- Define the R = Q x A equation regarding project success
- Describe the tools and techniques to assess and work with Stakeholders
- Describe the purpose and methods of communication planning throughout the life of a project
- Describe the role of the Alignment Model when facilitating teams
- Differentiate between Project Team roles and Meeting roles
Define Section
This section tests for understanding of what’s involved in conducting a successful Process Walk, and the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in the Define Phase.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Process Walks
- Define and describe the purpose of a Process Walk
- List the steps involved in a Process Walk from planning to results
- Describe the role of the facilitator, process walkers and interviewees
- List the pitfalls and ground rules involved in a Process Walk
- Leadership Skills
- Recognize the role of balanced feedback when coaching
- Describe the Socratic method
- List the common mistakes of the Define Phase
- Distinguish inquiry from advocacy
- Recognize different forms of inquiry
- List the tools and techniques involved in effective meetings (RACI, Agenda, Meeting evaluations, etc.)
- Recognize the elements to include in the Define Storyboard
Measure Section
This section tests for understanding of basic statistical terms and concepts as well as how to build the most effective data collection methods. It also tests for understanding of sampling strategies along with the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in the Measure Phase.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Continuous and discrete data
- Recognize why it’s important to know the difference
- Statistical Terms
- Differentiate between population and sampling symbols
- Define the different measures of center (mean, median and mode)
- Define the different measures of spread (range, variance and standard deviation)
- Define the P-Value and it’s role in statistical testing
- Normal Distribution
- Describe how it is different from other shapes
- Describe how to test a data set for normality
- Describe why and when normality is important
- Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
- Define the terminology and the process involved with ensuring an accurate data collection system
- Differentiate between the steps involved in MSA for discrete data vs. continuous data
- Recognize the pitfalls of conducting MSA
- Describe the meaning and ramifications of the output of an MSA
- Sampling
- Define the terms and process steps involved in developing a sampling strategy
- Describe the different sampling methods and strategies
- Describe the process involved in calculating sample sizes
- Process Capability
- Define the terms and calculations involved in assessing both discrete and continuous data
- Recognize the type of process capability calculation required given a sample scenario
- Leadership Skills
- Recognize coaching pitfalls in the Measure Phase
- Describe effective influence techniques for the Measure Phase
- List the different forms of decision-making available to a team along the advantages of each
- Recognize the elements to include in the Measure Storyboard
Analyze Section
This section tests for understanding of the hypothesis testing necessary to verify the root causes of waste and the best opportunities for improvement to the output or process “Y.” It also tests for understanding of the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in the Analyze Phase.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Hypothesis Testing
- Define and describe the purpose of formal hypothesis testing
- Define the terms and the process involved in formal hypothesis testing starting with a practical problem and ending with a practical solution
- Define the Null and Alternative hypothesis statements and how to write them
- Distinguish the appropriate hypothesis test required given data type, statistic and scenario
- Describe the meaning and practical ramifications of the output of hypothesis tests
- Differentiate between tests for normality, tests for difference and tests for correlation
- Define and describe the tests for continuous data with normal distributions, tests for continuous data with non-normal distributions and tests for discrete data
- Identify the role of risk in hypothesis testing
- Leadership Skills
- Recognize the coaching pitfalls in the Analyze Phase
- Describe techniques to reduce “Decision Fatigue” with Stakeholders
- Describe methods to prevent project team conflict
- Recognize the elements to include in the Analyze Storyboard
Improve Section
This section tests for understanding of how to plan and execute successful Designs Of Experiments in order to pilot and refine solutions to the root causes that were uncovered in the Analyze Phase. It also tests for understanding of the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in the Improve Phase.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Design Of Experiments (DOE)
- Define and describe DOE
- Define the terms and the process involved in conducting a DOE
- Differentiate between One Factor At a Time, Full Factorial and Fractional Factorial experiments and the pros and cons of each method
- Describe the meaning and practical ramifications of the output of a DOE
- Describe the role of Measurement Systems Analysis in conducting a DOE
- Describe the risks and pitfalls involved in conducting a DOE
- Differentiate between active and passive learning
- Leadership Skills
- Recognize the coaching pitfalls in the Improve Phase
- Describe the role of networking and how it increases the odds of project success
- List the tools and techniques to increase access to and feedback from Stakeholders and process participants
- Describe the facilitation methods to promote acceptance of the unknown and the role of criticism in brainstorming
- Recognize the elements to include in the Improve Storyboard
Control Section
This section tests your understanding of how to build an effective Monitoring and Response plan using the most appropriate Control charts for each Control Plan. It also tests your understanding of the role and use of Visual Management in process improvement along with the mentoring, influence and facilitation skills involved in the Control Phase.
A list of concepts, tools and techniques for this section:
- Control Charts
- Explain the way that Control Charts differentiate between Special and Common Cause variation
- Describe the connection between data distribution and the Upper and Lower Control Limits of Control Charts
- Describe how Control Charts can be used to design trigger measures in a Control Plan
- Identify the different components of a Control chart and give examples of tests for special cause variation
- Determine the appropriate Control Chart required given the data type, and data collection plan for a given scenario
- Interpret the results of a Control Chart
- Describe the meaning and practical ramifications of Control Charts that exhibit out-of-control conditions
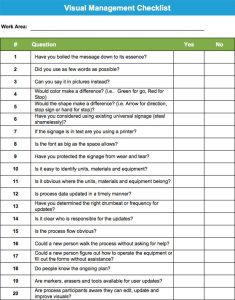
- Define and describe Visual Management
- Describe how and why Visual Management increases the success of process improvement
- List the guiding principles of Visual Management
- Describe the different uses of Visual Management
- Leadership Skills
- Recognize the coaching pitfalls in the Control Phase
- Identify the right influence or facilitation methods to use given an improvement team scenario
- Recognize the elements to include in the Control Storyboard