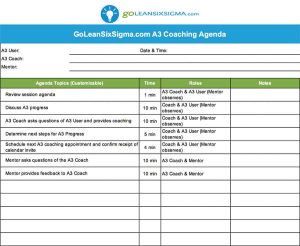
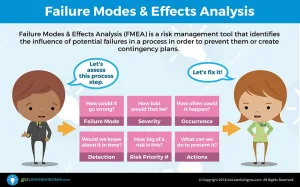
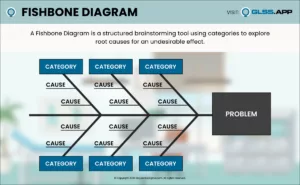
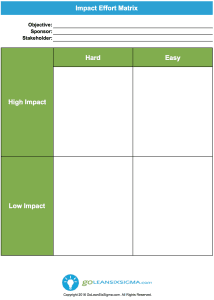
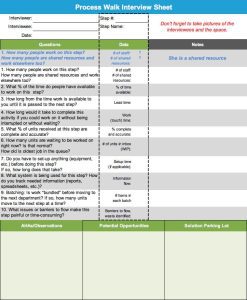
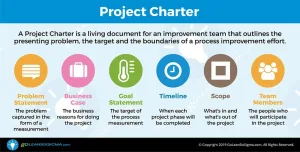
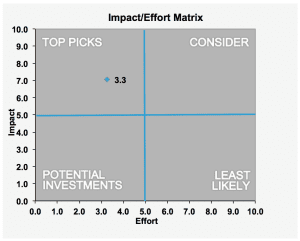
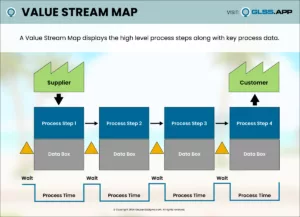
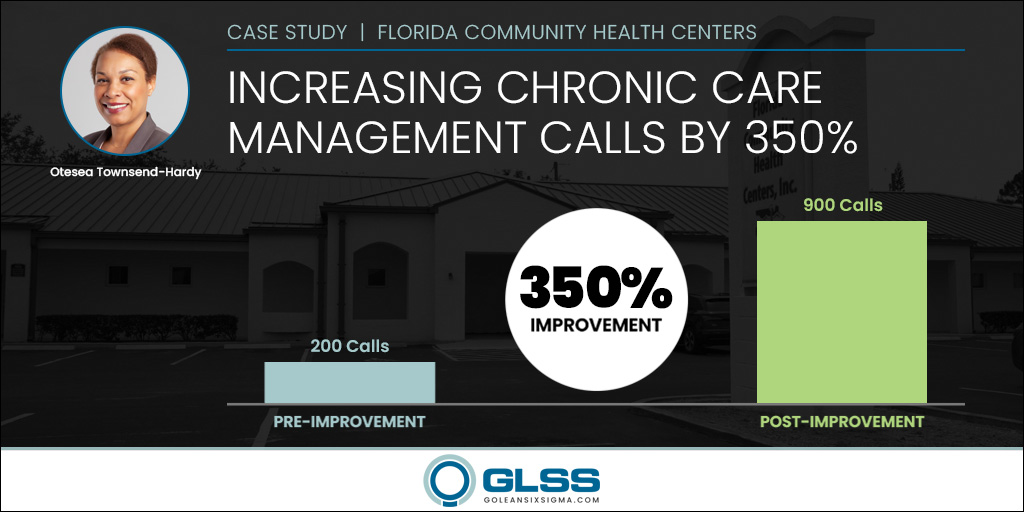
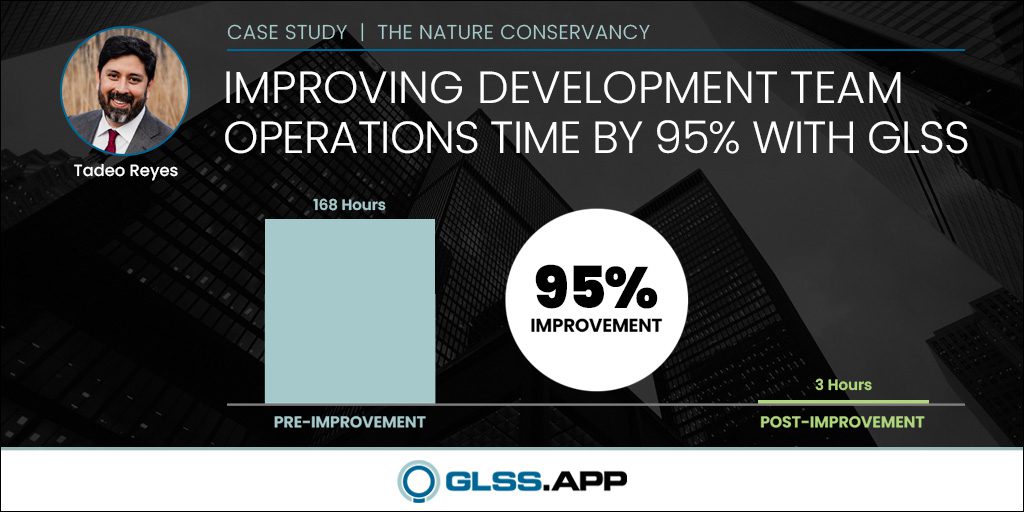
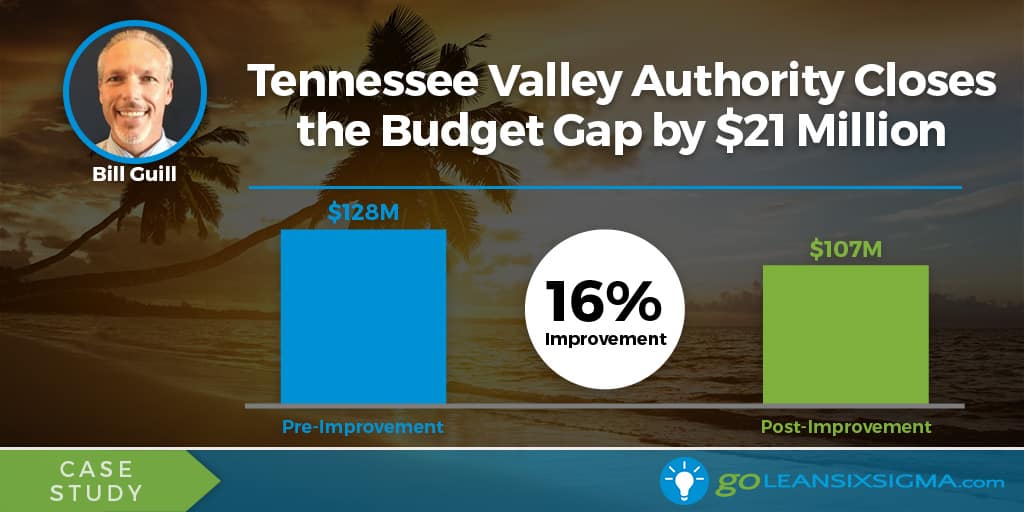
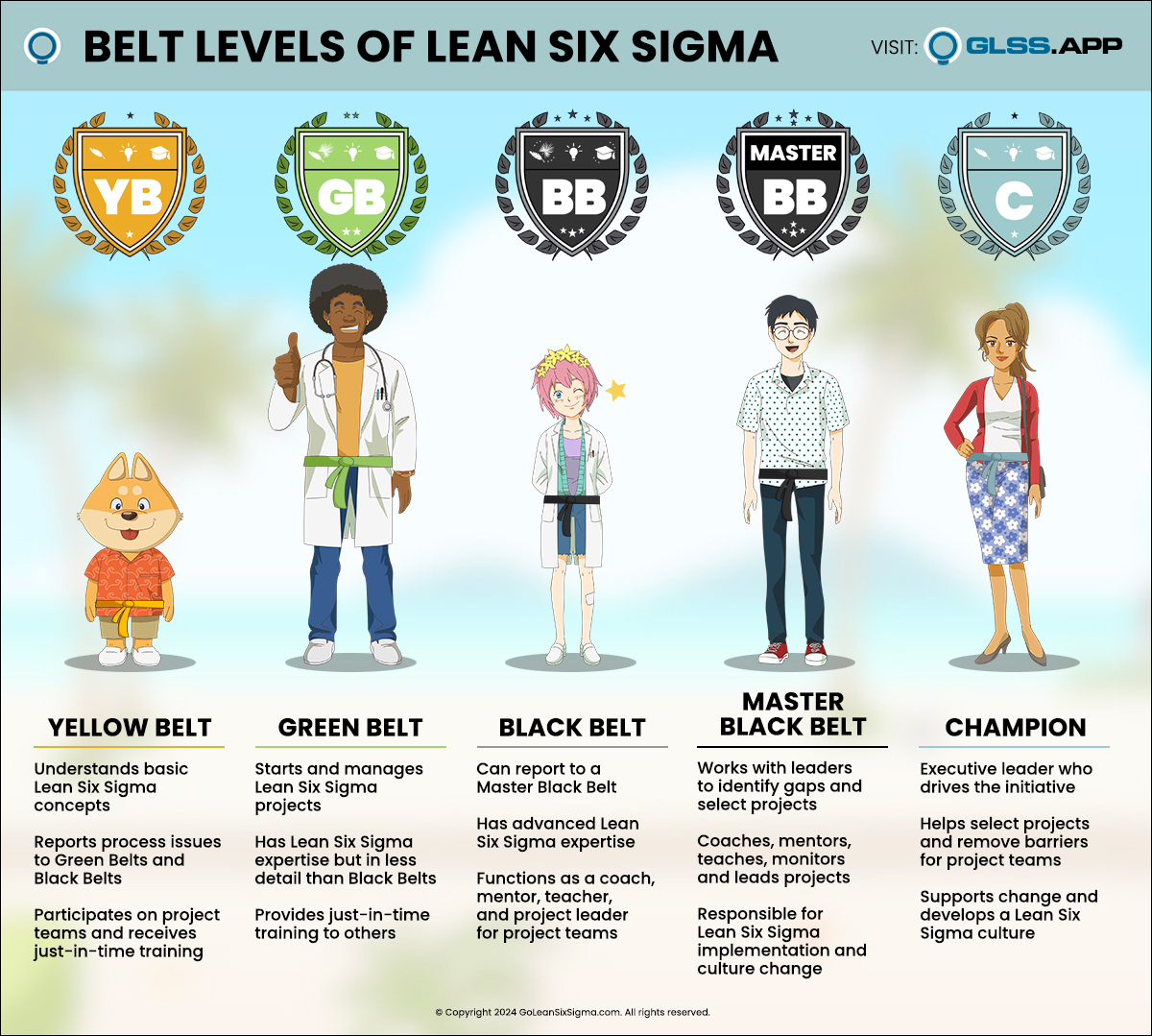
One of the most innovative methodologies in business processes is the development of Six Sigma. Since its foundation at telecommunications giant Motorola, Six Sigma has proven itself a forerunner in efficiency and excellence by focusing on standardization, cost reduction, and Continuous Improvement.
Let’s dive into the history of Six Sigma.
The Origin of Six Sigma
Six Sigma was pioneered in 1986 by American engineer Bill Smith. He developed it while employed at Motorola, as a revolutionary approach to quality improvement.
Six Sigma refers to a statistical benchmark, signifying a quality level that permits only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. In other words, it aids companies to deliver consistent, reliable outputs.
Early adoption of Six Sigma yielded impressive outcomes, including heightened product quality, decreased defects, and improved operational efficiency. Soon, industries worldwide enthusiastically adopted Six Sigma methodologies.

The Evolution of Six Sigma Methodology
Since the inception of Six Sigma, it has evolved, and been enhanced and transformed by organizations all over the world.
Here’s a brief Six Sigma timeline, by decade.
1980s
During the 1980s, Six Sigma came about as Motorola responded to a shift in the company’s need for a more systematic approach to quality improvement in its pocket pager. However, heralded as the father of Six Sigma, Bill Smith didn’t do this alone. Fellow engineer Mikel Harry and Motorola’s then-CEO Bob Galvin received co-credit.
Six Sigma was so successful for Motorola that the company was awarded the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award (the nation’s only Presidential award for performance excellence) in 1988.
Other companies noted this and implemented their own Six Sigma programs, such as IBM in 1989.
1990s
The 1990s saw some of the most significant growth and change for Six Sigma. Motorola registered Six Sigma as a trademark in 1993.
Mikel Harry left Motorola and founded the Six Sigma Academy, teaching and training employees for countless organizations.
Initially viewed as a system for manufacturing sectors, other industries like healthcare, finance, and service quickly transferred to Six Sigma principles.
Notable corporations saw the value and implemented their own Six Sigma programs, such as DuPont, Merrill Lynch, Bank of America, and Boeing.
Jack Welch, CEO of General Electric, was introduced to Six Sigma and became an enthusiast. He applied it company-wide at G.E. and achieved some of the most noteworthy and well-documented successes. Multiple NY Times-bestselling books detailing his success are available to read.
2000s
During the 2000s, Six Sigma saw significant expansion, refinement, and further standardization. It gained traction among global organizations outside the US, such as Sony, Jaguar, Samsung, and Adidas.
Companies began recognizing the complementary nature of Lean Manufacturing principles that Taiichi Ohno had championed at Toyota since the 1980s. As a result, they sought to combine the best of both programs, which evolved into Lean Six Sigma (LSS).
By 2005, Motorola claimed that their continual use of Six Sigma since beginning in 1986 had saved them over $17 billion–Proving the benefits of Lean Six Sigma.
2010s
In the 2010s, changing technological advancements and emerging trends led to greater integration with digital technologies. Companies began leveraging data-driven approaches, which enable accurate predictions for process improvement initiatives and real-time process monitoring.
Concerns of environmental sustainability and corporate social responsibility became pressing cultural issues, and LSS initiatives sought to meet those considerations. Projects began to emphasize minimizing waste by focusing on the 8 Wastes, reducing carbon footprints, and optimizing resource utilization.
Present
LSS continually adapts and optimizes to stay ahead. Organizations leverage big data, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to enhance the analytical capabilities of Six Sigma. This allows even deeper insights and more accurate predictions for process improvement initiatives.
One of the newest developments is the Agile project management methodology, which prioritizes responsiveness and adaptability. Agile focuses on quick and short-term improvements while balancing customer-centricity and cost reduction.
Hybrid approaches, such as Lean Six Sigma and Agile, enable organizations to balance structured problem-solving with flexibility and adaptability even more in project execution.
Soon it will be the 40th anniversary of Six Sigma, and this methodology is still expanding and—as it teaches—continually improving.
Learn more about how Lean Six Sigma can benefit you and your team through our free training.